Poultry Management and Farming Best Practices
Poultry farming is a cornerstone of agricultural production. It evolved significantly over the past couple of decades, transitioning from traditional methods to more sophisticated, technology-driven management practices.
In this article, we will look at how poultry management looks today — areas it covers, best practices, and technologies you can use to simplify poultry farm management.
What is poultry farming?
Poultry farming is a sector of agriculture that involves raising various types of birds — such as chickens, ducks, turkeys, and sometimes geese — for the purpose of farming meat or eggs for food. According to the US Department of Agriculture, the industry has been stagnating over the past few years, but the production is still near the all-time high.
Poultry is kept in a controlled environment which varies from large-scale indoor facilities to free-range settings. Farmers must carefully manage these environments to maintain the health and productivity of their flocks.
The success of a poultry farm hinges on the farmer's ability to adeptly manage these birds under varying agricultural and environmental conditions.
What does poultry farm management entail
Poultry farm management encompasses a broad array of responsibilities and tasks aimed at optimizing the productivity and welfare of birds under the farmer's care.
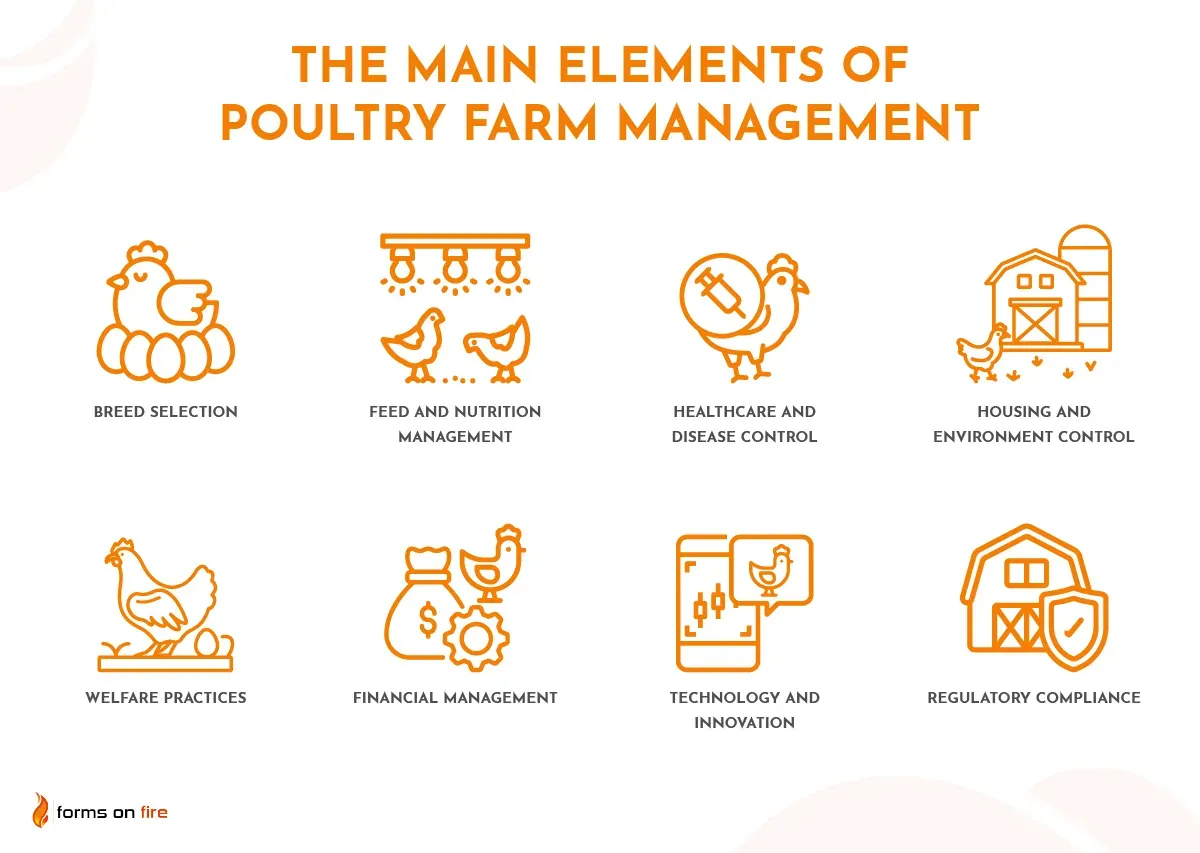
These include:
- Breed selection: Choosing suitable breeds for specific climates and market demands, and employing breeding practices that enhance desirable traits like disease resistance and high yield.
- Feed and nutrition management: Ensuring balanced nutrition that meets the birds’ growth and health needs, managing feeding schedules, and providing consistent access to feed and water.
- Healthcare and disease control: Implementing regular health checks, vaccinations, and strict biosecurity measures to prevent disease outbreaks and manage flock health.
- Housing and environment control: Designing and maintaining appropriate housing with adequate space, proper ventilation, and controlled temperature and lighting conditions.
- Welfare practices: Maintaining high welfare standards through humane handling and providing an environment that allows for natural behaviors.
- Financial management: Managing budgets, controlling costs, analyzing profitability, and planning strategically for farm expansion and reinvestment.
- Technology and innovation: Integrating advanced technologies such as automated systems and data analytics to streamline farm management.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring compliance with all relevant local, national, and international regulations regarding animal welfare, food safety, and environmental impacts.
These are all interconnected activities that need to come together in order to create a profitable and sustainable poultry farm.
Understanding poultry biology
Each species has unique anatomical and physiological traits that impact their housing, diet, health care, and handling requirements.
For example:
- Chickens require different care depending on whether they are raised for eggs or meat. Layer hens need high-calcium diets to produce strong eggshells, while broilers require energy-rich food for faster growth.
- Unlike chickens, ducks can tolerate colder temperatures but require good water management to prevent issues like wet litter.
- Turkeys are susceptible to heat stress and require more space and shaded areas, especially in hotter climates.
Understanding these differences is key to developing effective management strategies, leading to a more successful and humane poultry farming operation.
Poultry housing and environment
Creating an optimal living environment is essential for the health and productivity of poultry. Here are some factors to consider while designing poultry houses:
- Space: Adequate space per bird to prevent overcrowding, which can lead to stress, aggression, and increased disease transmission.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation systems to maintain air quality and appropriate humidity levels, crucial for respiratory health and comfort.
- Temperature: Temperature control systems to keep the environment within a species-specific comfort range, preventing heat stress or cold stress.
- Lighting: Controlled lighting that mimics natural light patterns helps regulate behaviors such as eating and roosting, and influences physiological processes like egg production.
Furthermore, a clean environment is critical to prevent disease and promote health. Regular waste disposal, cleaning, and disinfecting of the housing and equipment will reduce pathogen loads and minimize the risk of disease outbreaks.
There are various types of poultry housing. Roughly speaking, we could separate them into three categories:
- Conventional systems: Includes battery cages for layers and broiler houses for meat chickens. They are designed for efficient management but require careful oversight to ensure animal welfare.
- Enriched systems: Provide more space and enrichments like perches and scratching areas, improving welfare while maintaining productivity.
- Free-range systems: Allow birds outdoor access, promoting natural behaviors and potentially improving product quality. They require more physical space and robust biosecurity measures to prevent disease exposure.

Farmers are required to create a conducive environment that supports the health and productivity of their flocks while adhering to animal welfare standards.
Nutrition and feeding practices
Birds need a balanced diet tailored to their specific growth stages and production needs. In general, a balanced poultry diet includes:
- Proteins are crucial for growth, feather formation, and overall health.
- Carbohydrates provide energy.
- Fats are a concentrated energy source and are necessary for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
- Vitamins and minerals support physiological functions and prevent diseases. For example, calcium and phosphorus are particularly important for laying hens for strong eggshell production.
Water management
Water is the most critical nutrient for poultry. Clean, fresh water must be available at all times to maintain hydration and help with digestion and nutrient absorption.
As a part of water management, farmers need to:
- Select water sources
- Ensure water quality
- Maintain drinking systems to prevent microbial contamination
- Make adjustments based on temperature and humidity conditions.
Feed management
Proper feed management not only ensures that nutritional needs are met but also helps in reducing waste and managing costs. As a part of feed management, farmers need to stay on top of:
- Types of feed: Commercially prepared feeds are formulated to meet the specific nutritional requirements of different types of poultry at various stages of their life.
- Feeding schedules: Regular and consistent feeding schedules help maintain stable metabolism and growth rates.
- Feed quality: High-quality feed improves digestibility and efficiency, promoting better health and productivity.
- Proper feed line setup: Feed lines should be accessible to all birds, regularly cleaned, and free from contaminants.
You’ve probably heard the saying: “You are what you eat.” Well, the same goes for your flock. Cutting corners when it comes to feeding and nutrition is neither good for the flock, nor for the consumers of poultry products.
Poultry health management
Effective health management strategies are essential for preventing diseases, reducing mortality, and ensuring the welfare of the flock. Some of the best preventative measures include:
- Implementing a vaccination schedule.
- Routine health checks to help detect issues early.
- Regular cleaning and disinfecting of housing and equipment to help control the spread of pathogens.
- Isolating new or sick birds to prevent disease spread within the flock.
- Preventing contact between poultry and potential wild animal vectors.
- Ensuring that feed and water sources are uncontaminated and secure from pests.
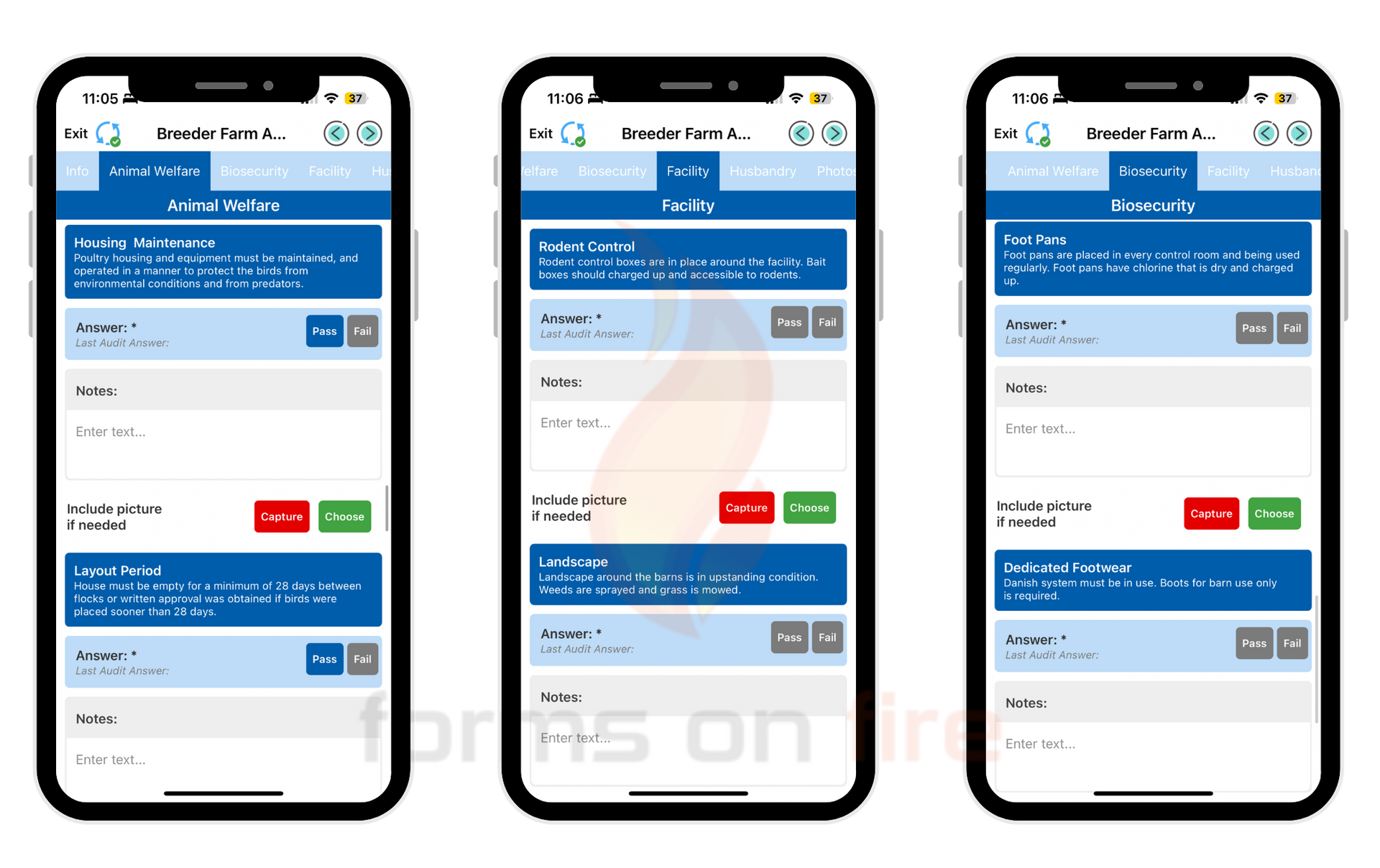
This is another area where Forms On Fire can help. You can use it to monitor environmental conditions, get reminders for vaccinations schedules, and track disease outbreaks and flock health.
Poultry breeding and genetic management
Breeding involves selecting birds with desirable characteristics and mating them to produce offspring that inherit these traits.
Through selective breeding, farmers can develop birds that are more efficient in terms of growth, egg production, disease resistance, and adaptability to environmental conditions.
Genetics plays a pivotal role in the success of breeding programs. Farmers need to understand which traits are heritable and to what extent they can be passed down to the next generation. These days, they can utilize DNA testing and other genetic technologies to precisely identify and select for beneficial traits.
Effective poultry breeding requires a combination of traditional and modern techniques like pedigree tracking, artificial insemination, and genomic selection.
Equipment and infrastructure management
A typical poultry farm will features all kinds of equipment like:
- Feeding systems
- Watering systems
- Automated systems for egg collection
- Ventilation, lighting, and other environmental control systems
- Poultry housing
Regular inspections and maintenance of equipment and infrastructure helps prevent breakdowns, prolongs their lifespan, and ensures they operate at optimal efficiency — promoting flock health and safety.
Keeping everything in good working condition year-round is easier said than done. This is why Forms On Fire comes with a bunch of pre-made templates farmers can use to inspect hen houses and hatcheries, create checklists and maintenance schedules for any piece of equipment, manage spare parts inventory, and much more.
Learn how to use Forms On Fire as your farm management software.
Using technology to improve the sustainability of poultry farms
With increasing regulatory pressures, poultry farmers need to pay special attention to sustainability and environmental footprints of their farms.
The latest standards in organic farming and poultry production focus on six key areas:
- Outdoor space requirements
- Indoor and outdoor living conditions
- Poultry stocking densities
- Maintaining preventative health care practices
- Physical alterations and euthanasia
- Transport, handling and slaughter
There are various equipment and software solutions that can help farmers live up to those standards. They can implement automated feeders and environmental control to ensure animal welfare.
To help prove compliance with various food and farm safety regulations, farmers should use software like Forms On Fire to create digital inspection forms and quickly generate required reports. This is also a great way to reduce the administrative load that comes with running a poultry farm.
The economic aspects of poultry farm management
To maximize returns and minimize costs, poultry farmers and farm managers need to carefully plan their budget and continuously track expenses. Major expenses include feed costs, labor costs, equipment costs, operational costs, and energy costs.
To enhance economic sustainability, poultry farmers can adopt various strategies like:
- Diversification: Expanding the range of products, such as selling both eggs and meat, or offering organic or free-range options, can tap into different market segments and increase revenue streams.
- Vertical integration: Controlling more stages of the production and marketing process can reduce costs and increase profit margins. For example, owning feed production facilities or direct selling to consumers.
- Innovation and efficiency: Investing in new technologies and practices that improve efficiency and productivity, like automated systems, can lead to long-term savings and higher outputs.
While there isn’t an universal approach that will work for all farmers, following best practices we outlined in this article will set you on the right track.
Simplify the administrative side of poultry management with Forms on Fire
Forms On Fire is a no-code platform anyone can use to create simple mobile forms and applications. Instead of using complex dedicated software solutions, farmers can use our platform to build only the forms and systems they actually need.
We have hundreds of pre-made templates and apps in our database for various poultry management tasks which can be easily copied and adjusted to specific needs. And our amazing customer support team is ready to jump in at any time to help you set everything up.
If you’re looking to digitize any poultry farm management process, look no further. For reference, here’s how Cal-Maine Foods used our platform to streamline on-site hen-house inspections, implement food traceability and egg counting, and improve operational efficiency.
Learn more by taking a free trial or scheduling a product demo.




